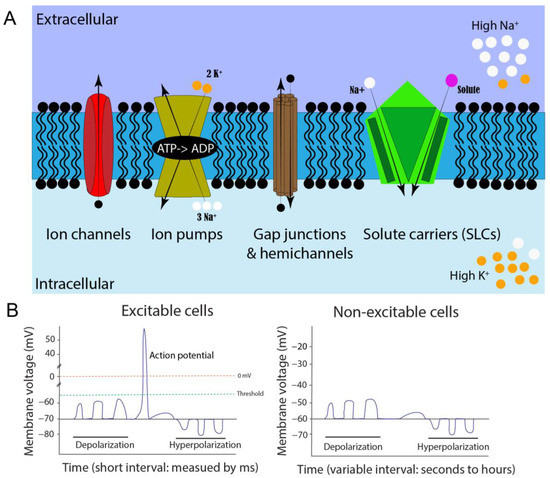
Developmental patterning is essential for regulating cellular events such as axial patterning, segmentation, tissue formation, and organ size determination during embryogenesis. Understanding the patterning mechanisms remains a central challenge and fundamental interest in developmental biology. Ion-channel-regulated bioelectric signals have emerged as a player of the patterning mechanism, which may interact with morphogens. Evidence from multiple model organisms reveals the roles of bioelectricity in embryonic development, regeneration, and cancers. The Zebrafish model is the second most used vertebrate model, next to the mouse model. The zebrafish model has great potential for elucidating the functions of bioelectricity due to many advantages such as external development, transparent early embryogenesis, and tractable genetics. Here, we review genetic evidence from zebrafish mutants with fin-size and pigment changes related to ion channels and bioelectricity. In addition, we review the cell membrane voltage reporting and chemogenetic tools that have already been used or have great potential to be implemented in zebrafish models. Finally, new perspectives and opportunities for bioelectricity research with zebrafish are discussed.
The intestinal bacteria of insects are crucial to the growth and development of the host. It has been found that various physiological processes of insects, such as immune response, metabolism, reproductive ability, and growth and development, involve the gastrointestinal flora. However, many external factors affect the composition of insects’ intestinal microorganisms, such as the type of dietary substrate. Sarcophaga peregrina (Robineau-Desvoidy, 1830) (Diptera: Sarcophagidae) is of great significance in medicine and forensic science. In this study, we investigated the effects of ciprofloxacin on the growth and gut microbiota of S. peregrina. The results demonstrated that the maximum body length of larvae was not affected by ciprofloxacin, while the growth rate of body length quickened as the concentration of the drug increased. The weight of the pupa and adult was reduced significantly due to the effect of ciprofloxacin. After analyzing the gut microbiota composition of S. peregrina in different drug groups, it was indicated that Ignatzschineria, Providencia, Wohlfahrtiimonas, Proteus, Myroides, and Bacteroides play important roles in the growth of S. peregrina. However, they still need to be further studied. In general, ciprofloxacin can affect the gut microbial community structure, which in turn affects the fitness of the host.

Microorganisms, Free Full-Text

What Is SEO and How Does It Work?

ACM Hack HOTH X: Intro to Git
Make sure your local business website and online profiles rank well and drive targeted traffic with our comprehensive local SEO guide.

Local SEO Guide: How to Rank on the First Page of Search Engines
Out of package, no box. Figure is in excellent condition. 5” figure. All parts shown.

Mattel Vintage Masters of the Universe Mosquitor
Parts: 821PCS Designed and Authorized by jellco With PDF instruction

MOC-84723 Battle Of HOTH: Walker Attack Universe War Scene Set by jellco

Final 2022 Statistics - Users Edition

Jasper Street Co. – Another Day (2003, Vinyl) - Discogs
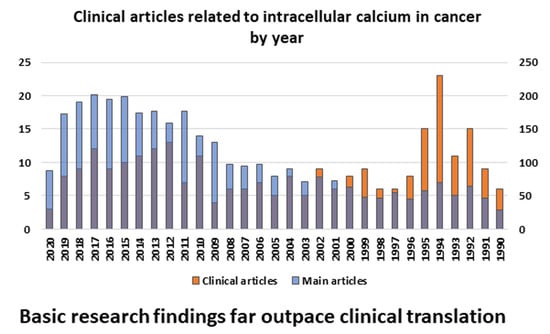
Intracellular Ca2+ distribution is a tightly regulated process. Numerous Ca2+ chelating, storage, and transport mechanisms are required to maintain normal cellular physiology. Ca2+-binding proteins, mainly calmodulin and calbindins, sequester free intracellular Ca2+ ions and apportion or transport them to signaling hubs needing the cations. Ca2+ channels, ATP-driven pumps, and exchangers assist the binding proteins in transferring the ions to and from appropriate cellular compartments. Some, such as the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, and lysosomes, act as Ca2+ repositories. Cellular Ca2+ homeostasis is inefficient without the active contribution of these organelles. Moreover, certain key cellular processes also rely on inter-organellar Ca2+ signaling. This review attempts to encapsulate the structure, function, and regulation of major intracellular Ca2+ buffers, sensors, channels, and signaling molecules before highlighting how cancer cells manipulate them to survive and thrive. The spotlight is then shifted to the slow pace of translating such research findings into anticancer therapeutics. We use the PubMed database to highlight current clinical studies that target intracellular Ca2+ signaling. Drug repurposing and improving the delivery of small molecule therapeutics are further discussed as promising strategies for speeding therapeutic development in this area.
Biomedicines, Free Full-Text
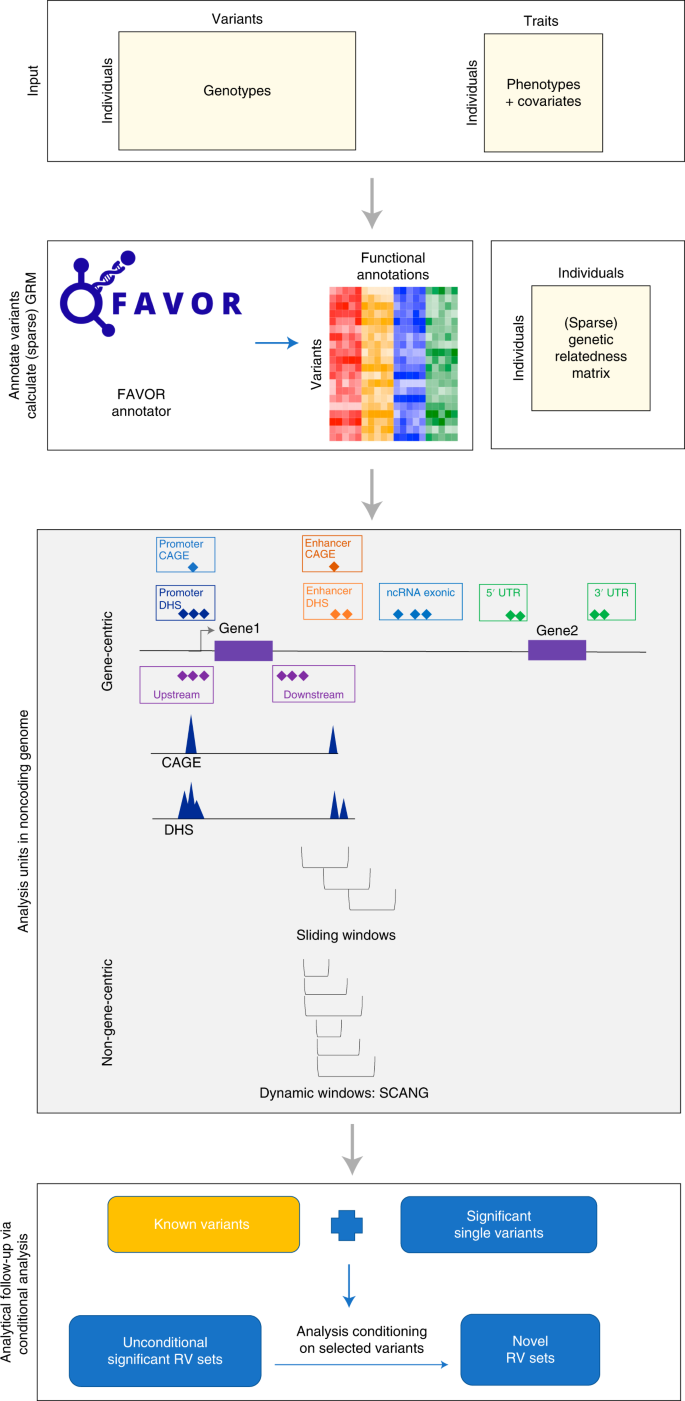
A framework for detecting noncoding rare-variant associations of large-scale whole-genome sequencing studies

Luke Skywalker™ (Snowspeeder Pilot) Sixth Scale Collectible Figure by Hot Toys

Google Rank Checker Tool (Check Your SEO Rankings)

Star Wars The Empire Strikes Back Han Solo (Hoth) Mini Set LEGO 5001621 [Bagged]

John Williams, The London Symphony Orchestra – Star Wars / The Empire Strikes Back (1980, Vinyl) - Discogs